When planning the installation of new businesses WISP entrepreneurs generally follow a centralized network design, first building a network operations center (NOC), where the wholesale Internet connection and network management equipment is installed. The NOC is connected to point to multi-point (PtMP) wireless towers with point-to-point wireless links, and the PtMP towers provide a wireless connection for the customer premise equipment (CPE) wireless units.

Once the network operations center has been built and tested then PtMP towers can be built out and connected back to the NOC with the point-to-point (PtP) wireless distribution network. The WISP should take advantage of towers that are already built and lease #tower space to begin operations quickly. There are service companies that operate mobile phone #antenna towers that are suitable for the #installation of WISP antennas. If the WISP has to construct towers then there will be an additional investment and further delays before the business can begin operations.
The figure below shows the basic plan of the WISP’s network.
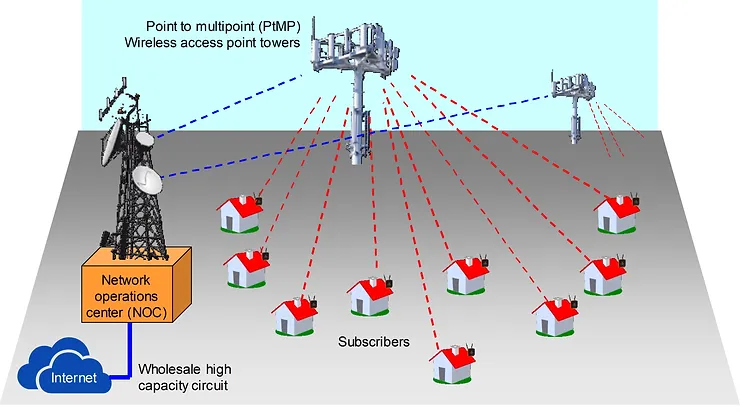
With the first PtMP tower in place the WISP can begin offering Internet services to prospective customers. The WISP will have calculated a minimum number of subscribers to achieve the business cash flow break-even number of subscribers and so the WISP must push sales quickly to acquire the minimum number of #subscribers.
Next the WISP must begin increasing the number of towers to reach the maximum number of subscribers that can be supported by the NOC infrastructure and the capacity of the wholesale circuit to maximize profitability. Once multiple towers have been installed and the capacity of the #network operations center and wholesale circuit has been reached then the WISP has to move from growing to a cost optimization mode in order to improve business profits. This will mean making business processes more efficient to handle the workload with less staff. The number of subscriber installations will reduce to maintenance levels with only the replacement of subscribers who have discontinued service.
If the WISP desires to continue expanding then the NOC has to be upgraded with more wholesale circuits. If the NOC capacity is expanded then PtMP towers have to be constructed further from the NOC to expand the area of coverage, which requires more relay/repeaters. A better technical solution may be to build a second NOC close to the new area of coverage.
There is an alternative WISP business development strategy that speeds time to begin delivering the service to subscribers. Many towers are built for mobile phone providers and the tower operators lease space for #WISP antennas. The towers have a fiber Internet connection and back-up power. The cost of the tower space is higher than an antenna tower without services however there is no other cost for the WISP. The access control router is installed at the tower and connected to the fiber circuit router. The NOC is eliminated and the PtP wireless distribution network between the tower and the NOC is eliminated. See the next illustration.
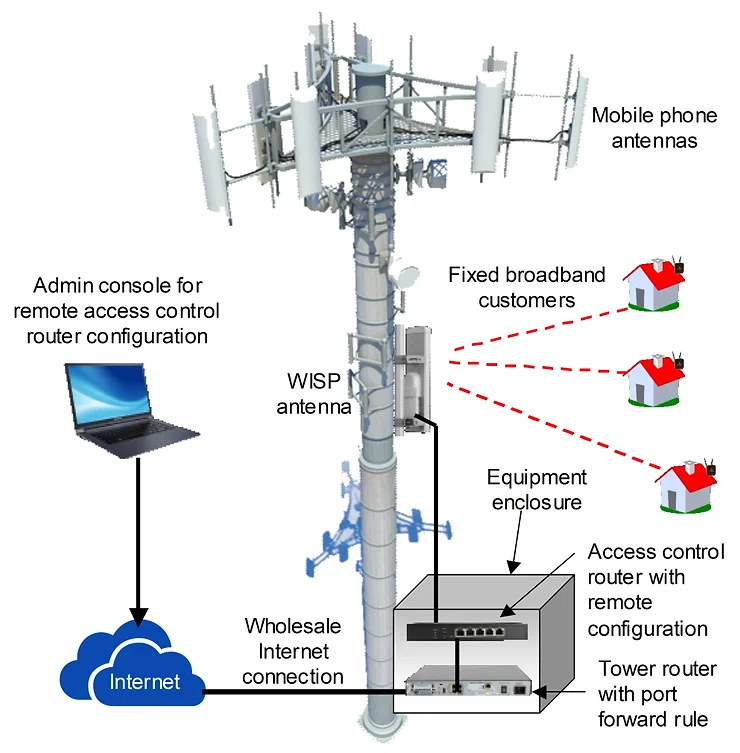
The access control router is accesses remotely via the Internet to configure subscribers and rate plans. Some WISP management system like easyWISP (www.easywisp.com) are designed to manager distributed access control routers and make the process of managing subscribers very easy, a few UI click using an advanced management Interface.
______________________________________________________________________
Readers are invited to share this information with others. If any reader has a question regarding this information please contact us via our contact page.
